Linux Database Security Tips

Data leaks are extremely prominent in the cyber world due to lack of proper or adequate security implementation. Securing databases is an essential practice to ensure that consequences such as data loss to even unauthorized access or system downtime is avoided.
There are many challenges when it comes to database security, as the more accessible a database is, the less secure it is. Some of the common security challenges when it comes to database security include human error, malware, physical location security, and software vulnerabilities. However, there are many steps that can be taken to ensure that a database is secured, and therefore avoid any of the issues mentioned above. Moreover, database encryption is an essential step in securing all data.
Linux has a variety of tools that can be used to guarantee database security. In this article, we will be introducing some of these tools that can be used for database assessment and others that will help in securing these databases.
MySQL & MariaDB Database Best Practices
MySQL and MariaDB are some of the most popular database servers used today. While the flexibility and scalability of these servers make them very popular choices among organizations of all sizes, they still have security issues that can be discovered and exploited by attackers.
Some of the common security threats include DDoS attacks, SQL injection attacks, Man in the Middle attacks, weak passwords, data corruption, race condition, mismanagement of account access, as well as the occasional vulnerabilities. Fortunately, there are many practices that can be adopted to be able to avoid these security concerns.
Encryption
Encryption is one of the most effective and important practices that should always be used when storing data. MySQL and MariaDB can both encrypt the data directly or encrypt the container it is held in. For MySQL, some of the tools that can be used for encryption are asymmetric encryption, symmetric encryption, public/private key generation, digital signatures, and transparent data encryption. As for MariaDB, there is at-rest data encryption, in-transit data encryption, TLS/SSL certificates, and Cipher Block Chaining.
Moreover, to ensure database security, other useful practices to keep in mind are conditional access, and auditing. For conditional access, it is always useful to apply least privilege. It is very important to only grant the least amount of privileges needed for a user to be able to complete the job. As for auditing, there are a range of tools that can be used to audit databases such as ClusterControl and Cloud SQL for MySQL, while MariaDB has its own audit plugin that can be used.
Restrict Access & Customize Default Settings
The next steps to take to secure a MySQL database should include removing default accounts, port mappings, and customizing default settings. It is very critical to remove the test database as all users have full access to it.
Remote access should also be restricted. Network access should only allow the minimum required, as is the case for many security practices, including the mentioned least privilege approach. All remote access should be monitored and controlled.
Ensure that Servers Are Physically Secure
An important step that is frequently ignored is making sure the servers are physically secure. If you are using cloud providers such as AWS, GCP, or Azure this is automatically covered.
One of the most essential steps in securing anything, not just databases, is ensuring the use of strong authentication credentials. Weak passwords can be easily brute-forced granting attackers access to the servers. Therefore, make sure only strong passwords are used that contain a mix of upper-case and lower-case characters, numbers, and special characters.
Moreover, authn and authz, which refer to authentication and authorization, allow you to control user access to elements within the database.
Use Database Security Assessment Tools
A critical step to take to secure a database is using database security assessment tools. These tools review the environment of a database and recognize the threats that are present in the environment. Other than just highlighting the existing vulnerabilities present in the environment, these tools also assess the implemented security measures to check for effectiveness. I will be introducing five of the top Linux database security assessment tools to use for ensuring you have a secure database.
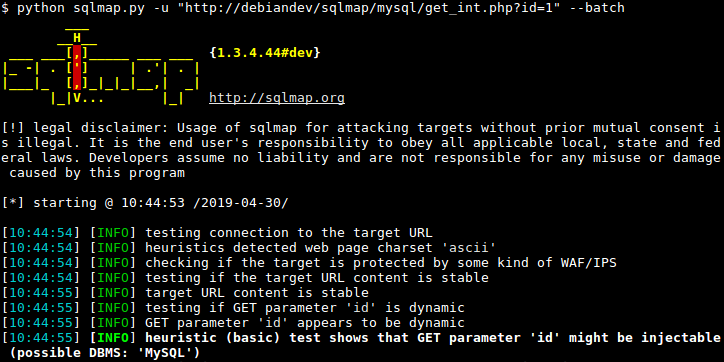
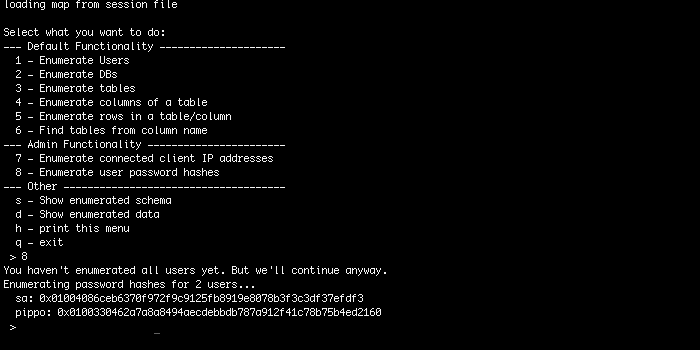
SQLMap
SQLMap is a python-based open-source SQL injection tool. This is a great tool to use as it offers a variety of features. These features include detecting and exploiting different types of injection attacks, brute-forcing password hashes, uploading or downloading files from the database, can be used to directly connect to the database through SQL injection, and is customizable.
SQLNinja
SQLNinja is a Perl-based tool that can be used with applications using Microsoft SQL servers as their backend for exploiting SQL injection vulnerabilities. SQLNinja features include the ability to fingerprint remote SQL servers, data extraction, upload executables, exploit injection vulnerability to gain access to the database, brute-force passwords using dictionary attacks and privilege escalation attacks if brute-force is successful.
BBQSQL
BBQSQL, like SQLMap, is an open-source python-based tool. BBQSQL is used to exploit SQL injection vulnerabilities and focuses on blind SQL vulnerability. This tool requires certain information to be used, which include URL, HTTP method, cookies, and so on. However, it is a great tool as it is very fast in finding and exploiting vulnerabilities, it is customizable, it carries out input validation on all configuration options, and it can even patch the detected vulnerabilities.JSQL Injection
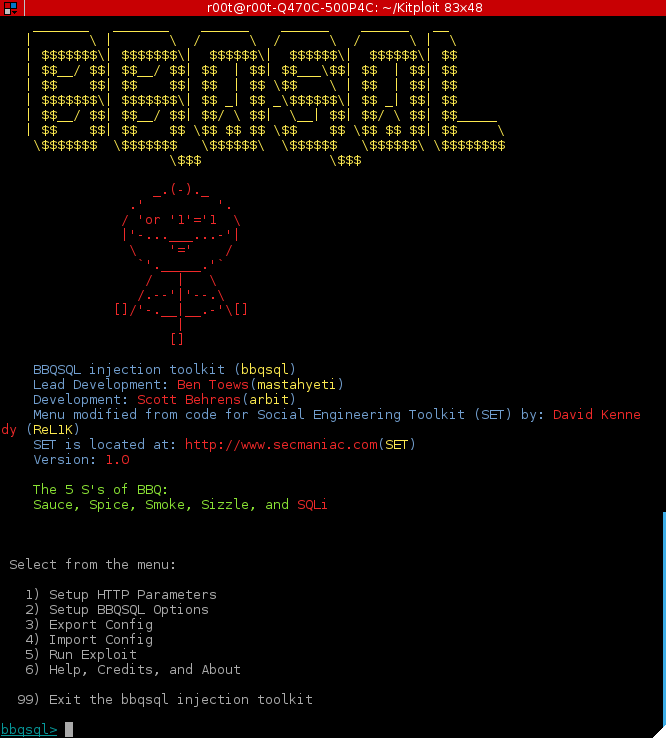
JSQL Injection, as the name indicates, is also an SQL injection tool that is java-based. It can be used to find and exploit injection vulnerabilities. It can be used across 33 database engines, carry out multiple types of injection attacks, create a web shell and SQL shell on a remote server, used to brute-force hashes, and much more.
OScanner
OScanner is an Oracle assessment framework that is java-based. It can be used for SID enumeration, brute-force passwords, enumerate version, account roles, privileges, and password policies, audit information, and database links. OScanner gives the results in a graphical java tree format.
These tools that we have mentioned are critical in ensuring that your database is secure. They can be used to check what steps need to be taken to make sure databases are secure, and they can also be used after taking these steps to evaluate the effectiveness of the procedure followed.
Installing, Configuring, & Securing MySQL &MariaDB Databases
To install the database, start with typing sudo apt-get install mysql-server in the command line. Once that is complete, type sudo mysql_install_db. Next, run sudo mysql_secure_installation. This step is essential as it will remove some defaults that present security threats. Once that is complete and the database is installed, we can start on the next steps to improve security of the database.
To begin with, we need to change some settings in the my.cnf file which is the main configuration file for MySQL. To do that, we first run sudo nano /etc/mysql/my.cnf. Make sure that the server is not accepting connections except from the local machine by checking the bind address setting, which should be bind-address = 127.0.0.1. A more secure way to connect to other machines would be through SSH. Next, we will be adding local-infile=0 to patch a vulnerability that allows access to the underlying file system.
 As we have mentioned previously, a security practice that should be implemented is auditing. While there are many tools to do that, we can do it by adding log=/var/log/mysql-logfile. The log files should not be world readable by running sudo ls -l /var/log/mysql*. This will show the permission for the log files. If you want to change those permissions, you can do that by using the chmod command. However, as mentioned before, least privilege should be applied and users should only be granted the minimum access needed.
As we have mentioned previously, a security practice that should be implemented is auditing. While there are many tools to do that, we can do it by adding log=/var/log/mysql-logfile. The log files should not be world readable by running sudo ls -l /var/log/mysql*. This will show the permission for the log files. If you want to change those permissions, you can do that by using the chmod command. However, as mentioned before, least privilege should be applied and users should only be granted the minimum access needed.
Moreover, there are more steps that can be taken while using MySQL to improve database security. After logging in by typing mysql -u root -p and entering the password, start by securing passwords and host associations. This is done by first making sure there are no users that do not have a password. Run SELECT User, Host, Password FROM mysql.user;. If the results return a user with no password, you can add a password by running UPDATE mysql.user SET Password=PASSWORD(‘newpassword’) WHERE User=”user-name”;.
While the steps taken to install the database should have eliminated any blank users, we can still make sure there aren’t any of them by running DELETE from mysql.user WHERE User=’’;. Once we are done running the previously mentioned commands, we run FLUSH PRIVILEGES; to implement the changes.
If you want to change the specific permissions for specific users, this can be done by running GRANT SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE ON dbname.* to ‘username’@’localhost’;. To change these permissions we can run something like REVOKE UPDATE ON dbname.* FROM ‘username’@’localhost’;. The command FLUSH PRIVILEGES; needs to be run in order to implement the privilege changes. To check for the current user privileges, you can run SHOW GRANTS FOR ‘username’@’localhost’;.
Another practice that could be very helpful in ensuring a database is secure is changing the username of the root user. This will help by making the attacker have to go through a lot more to be able to find the new username rather than just use the preset name of “root”. To do that we can run rename user ‘root’@’localhost to newusername’@’localhost’;. Like the previous commands, FLUSH PRIVILIGES; needs to be run to implement the change.
Conclusion
As I have mentioned, data breaches and leaks are one of the most prevalent cyber incidents. These leaks include all types of sensitive data that should not be revealed. There are many steps that can be taken to ensure Linux database security, and therefore, avoid data breaches or leaks.
These steps include best practices that are useful in ensuring a safe and secure database server by auditing, encryption, and other methods which include applying least privilege, using strong credentials, removing default accounts, port mapping, restricting remote access, physically securing servers, and changing default settings.